Combinatorial Analytics & AI
Providing the most reliable, reproducible and detailed understanding of disease on the planet

Characterizing disease by molecular mechanism
Chronic diseases present the greatest challenge to human health. They're caused by a complex interplay of biology, which gold standard genomic analysis and AI models are unable to detect.
Our hypothesis-free combinatorial analytics platform is uniquely able to reveal how multiple genes and other factors interact to cause complex diseases. Identifying the mechanisms specific to each patient to personalize care and improve health outcomes.
Our platform is unbiased and infinitely scalable, producing findings that are reproducible and explainable – making new discoveries faster than ever, with the highest level of confidence.
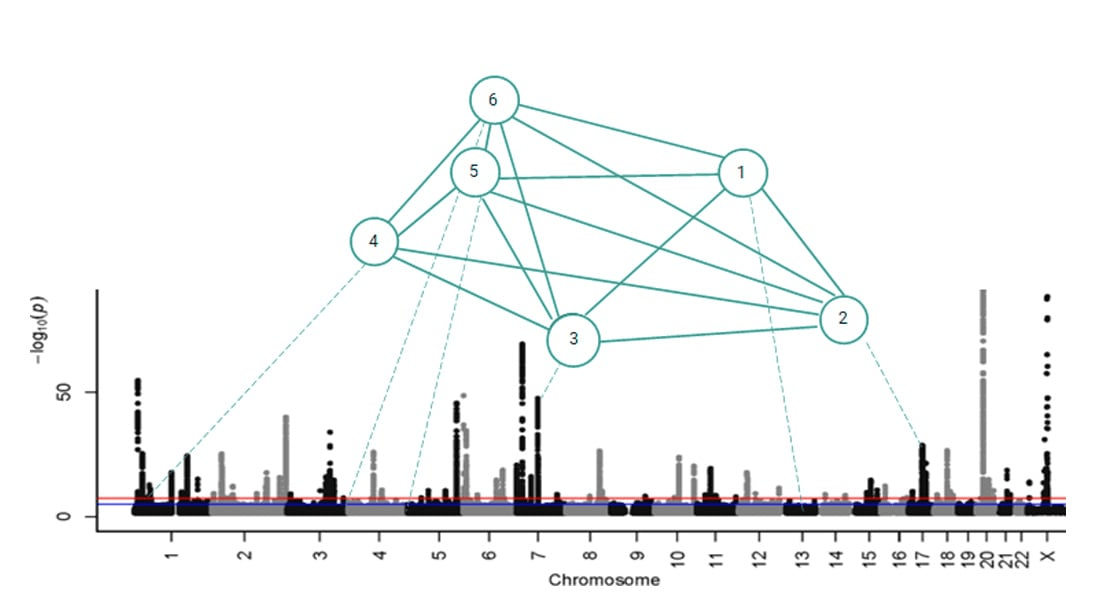
Combinatorial disease signature comprising six co-associated SNPs

Going far beyond all AI & data models
LLMs and other AI models are limited by their training sets, which are massively biased and too incomplete to address the challenge of chronic disease biology.
Combinatorial analytics enables us to rapidly analyze multiomic datasets at massively higher orders of combinations – far more than is possible with even the most advanced AI methods.
Only we find the effects of combinations of features and capture non-linear signal in the biology of genetic and metabolic networks – revealing the deepest insights into disease biology to de-risk every stage of drug development and clinical care.
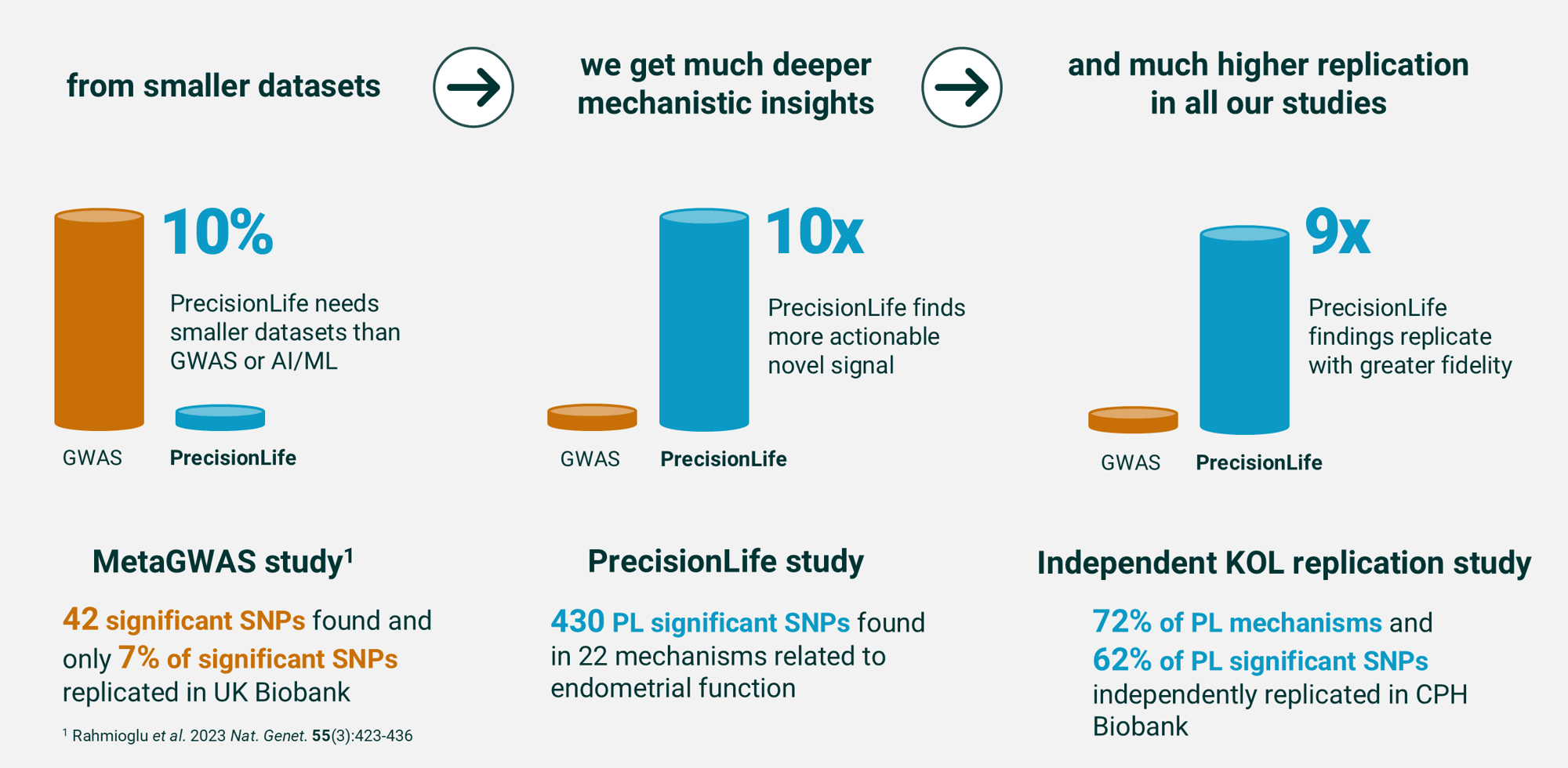
Deeper disease understanding & replication
Combinatorial analytics identifies significantly more mechanistic insights, from less data, with considerably greater replication than any other analytical method.
The graphic below shows this in a direct comparison between the PrecisionLife platform and a meta-GWAS of endometriosis patient data, published in Nature Genetics¹ by an international consortium of key opinion leaders.
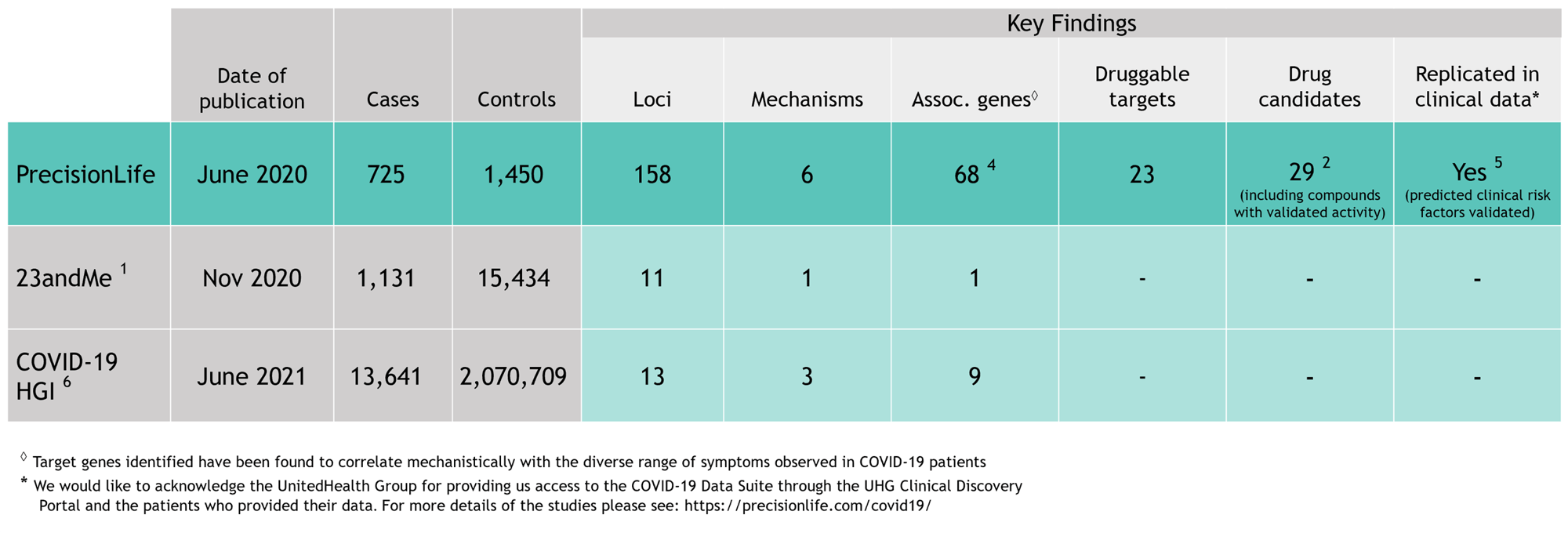
Informing R&D & healthcare with greater insights, faster
Our combinatorial analytics & causal AI platform outperformed global efforts to identify genetic factors for severe COVID-19 susceptibility, producing more proprietary insights, novel clinical biomarkers, and novel drug targets than any other analysis.
Completed 12 months earlier than the COVID-19 Host Genetics Initiative, our analysis identified many more loci and genes associated with severe COVID-19 than any study before or since.
We found 68 genes associated with severe COVID-19 and linked them all to major symptoms of the disease. These findings have since been extensively validated by our collaborators and independently by other groups around the world.
Analyzing every possible combination to find the cause
We incorporate a wide range of multimodal data types, singly or in combination, to identify features that in combination are associated with a phenotype.
This allows us to generate much more and far richer signal from smaller datasets than traditional Genome Wide Association Studies (GWAS) models and to better stratify patients according to the mechanistic origins of their disease.
● Genomics - e.g. genotype array, low-pass or clinical grade WGS
● Epidemiological - e.g. social determinants of health (SDOH), age, BMI, diet
● Environmental - e.g. SDOH, pollution, stress
● Phenotypic - e.g. disease severity, progression, therapy response
● Clinical - e.g. history, co-morbidities, prescriptions, claims, lab results, assays
● Real world evidence - e.g. incidence & outcomes for indications
● Transcriptomics - e.g. RNA Seq, single cell expression, epigenetics, Hi-C, OCRs
● Metabolomic - e.g. liquid biopsy, blood analytes
● Digital biomarkers - e.g. activity sensors, continuous glucose monitoring
● Imaging - e.g. diagnostic features called by AI from MRI/CT
● Pathogens - e.g. strains, counts
● Structural variants - e.g. CNVs, splice variants
● Microbiome - e.g. counts, gut, skin, nasopharyngeal, taxa profiles



