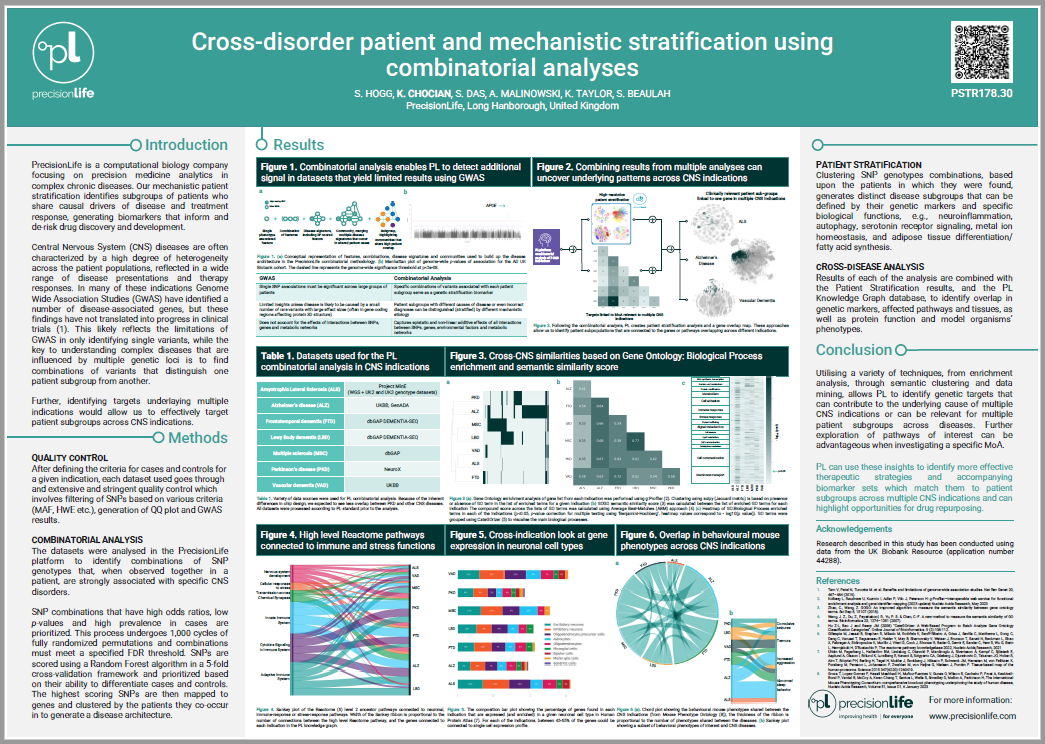
Central nervous system (CNS) disorders encompass a broad spectrum of conditions that share some common characteristics including clinical phenotypes such as cognitive dysfunction, sleep disturbance and mood changes. This suggests the existence of shared pathophysiological mechanisms that can provide insights into development of common therapies. Genetic studies aiming to identify common mechanisms across CNS disorders are constrained by the limitations of GWAS approaches which typically identify isolated genetic variants with high prevalence.
The key to understanding complex, multi-symptomatic CNS syndromes influenced by multiple genetic loci, epidemiological and/or environmental factors is to find combinations of these factors in sub-cohorts with distinct characteristics. We use a hypothesis-free method for the detection of combinations of genetic factors that together are strongly associated with variations in disease risk, symptoms, prognoses, and other disease-associate variables in patient subgroups.
Patient stratification insights generated by these combinatorial disease signatures enable identification of mechanistic subgroups that are common to multiple indications. The PrecisionLife platform was used to compare disease to control and identify common genetic variants across a wide range of CNS indications; subsequent enrichment analyses were performed to determine pathways and biological processes that are significantly associated with the genetic variants identified for each indication. This enabled us to identify biological mechanisms that are impacted across CNS diseases.
Our results identified multiple common biological processes that are significantly affected in several CNS diseases such as neurogenesis, neurotransmission, cell death signalling and lipoprotein metabolism; 78 disease-associated genes were identified in two or more different CNS indications, including 22 enzymes, 10 transcription factors and 9 transporters. Combinatorial analyses can stratify heterogenous patient populations with complex pathologies to identify mechanistically driven stratification insights that classify patients beyond traditional syndromal diagnostic categories.
Our analyses indicate that subgroups of patients with CNS diseases have common pathophysiological drivers that may contribute to specific common clinical manifestations; the patients in these subgroups can be identified using combinatorial genetic patient stratification biomarkers, to enable a targeted precision approach to symptoms occurring across multiple CNS disorders.
Find out more